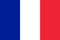
The group of infectious diseases includes a fungus on the legs, which is a type of yeast infection. This pathology is caused by microscopic fungi. Nail plaque disease is called onychomycosis.
<1_img_centerxx>Fungal lesion of the feet
It is a very common condition in both men and women. The most common types of yeast infection are:
- trichophytosis;
- candidiasis;
- epidermophytosis.
Some fungi can infect both animals and humans. It is necessary to know not only what yeast infection is, but also why it develops. The main mechanism of human infection is contact. It is carried out directly and indirectly. In the first case, the fungi get on the feet in contact with soil, plants or a sick person. Familial infections have been reported.
Indirect transmission of the pathogen is carried out during contact with animal care items and personal belongings of patients. These can be shoes, towels and scissors, as well as bath accessories.
The transmission factors are often socks, stockings and other personal items. Foot fungus can develop after visiting public baths and swimming pools. The process involves both the skin of the legs and the nail plates.
The contributing factors are:
- increased sweating of the legs;
- the presence of corns and abrasions;

- wear tight shoes;
- non-observance of personal hygiene;
- wearing someone else's shoes;
- accommodation in youth hostels;
- weakened immunity;
- bad nutrition;
- the presence of other skin diseases;
- hypovitaminosis;
- Alcohol addiction;
- smoking;
- walk barefoot;
- Endocrine disorders.
Debilitated people are more likely to face this problem.
General clinical manifestations
The fungus on the soles of the feet and toenails can go unnoticed for a long time. With this disease, the following symptoms are observed:
- peeling of the skin;
- drought;
- the presence of diaper rash;
- thickening of the skin and nail plates;
- brittle nails;
- redness;
- itching;
- white or yellowish bloom;
- the presence of erosion;
- skin pain.
The fungus on the feet is different. It all depends on the type of pathogen and the underlying disease. Sometimes an unpleasant smell leaves a person. The fungus on the foot does not lead to deterioration of the general condition. Symptoms of poisoning are absent, since fungi are conditional pathogens and are localized in the surface layers of the skin.
One leg is affected first. Then the mushrooms are introduced into the second limb. Most often, the following areas are involved in the process:
- back of the foot;
- spaces between 4 and 5 fingers;
- nail plates.
Depending on the clinical signs, the scaly, dyshidrotic and intertriginous forms of the disease are distinguished. In the first case, scales appear on the reddened skin. A coat is observed. Itching is an intermittent sign. It doesn't bother all the patients. With a dyshidrotic form of mycosis, bubbles appear on the fornix. They can get bigger. After a few days, they are open. Erosion appears in their place. An area of diaper rash appears. As the erosion dries up, peeling is observed.
In the event that the fungus of the skin of the feet becomes complicated with a bacterial infection, the exudate becomes purulent. Pain appears. Fever is possible. Fungal infection sometimes causes the development of an intertriginous mycosis. Its main feature is the presence of cracks with a white edge. The seepage develops over time. Pain appears. Erosion forms in the area of the cracks. This form of the disease occurs in a chronic form with exacerbations in the summer.
Development of onychomycosis of the legs
With the fungus on the feet, onychomycosis can be found. With it, the nails are involved in the process. The prevalence of this pathology in the population is 10 to 20%. In recent years, the incidence of the disease in children has increased. Fungi actively grow and multiply not only on the skin, but also on the nail plates.
People with varicose veins, hyperhidrosis, flat feet, and endocrine diseases often face a similar problem. Fungi multiply inside the nail, gradually leading to its destruction. If the disease is not cured, it can last for years. The end result is the detachment of the nail. Hyperkeratosis often develops.
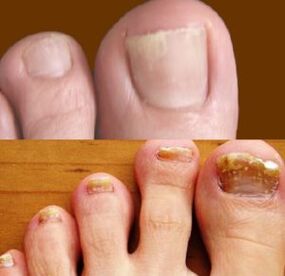
Distinguish between hypertrophic, normotrophic and atrophic onychomycosis. In the first case, the nail becomes dull and thickens. With atrophy, the color of the plaque turns brown. His detachment is observed. With normotrophic onychomycosis, the shape and size of the nail does not change. With the development of onychomycosis on the feet, the following symptoms are observed:
- decrease in nail density;
- change its color;
- the presence of white or yellow spots;
- itching;
- Cracked skin;
- peeling;
- thickening of the plaque;
- increased fragility.
If the treatment for nail fungus is not carried out, there is a risk of developing paronychia. In this condition, purulent inflammation of the nail bed occurs.
Examination and treatment tactics
You need to know not only how the fungus starts on the foot, but also how to get rid of it. The treatment regimen is determined by the attending physician. Before that, the following studies will be necessary:
- inspection with a wood lamp;
- microscopy of scrapings;
- general clinical analyzes;
- sowing on nutrient medium.

Differential diagnosis is made with psoriasis, onychodystrophy, lichen planus, congenital pachyonychia, trauma and eczema.
Any experienced dermatovenerologist knows how to treat nail fungus. Antifungal drugs are used in the form of solutions, creams and varnishes.
Treatment for toe fungus often involves surgery. The affected nail is removed.
In the event of long-lasting epidermophytosis, a systemic remedy for mycosis of the foot based on miconazole or ketoconazole may be prescribed. Proper treatment will kill germs. There are products on sale that adapt to the passage of the affected nail plates. They come in the form of patches.
To increase the effectiveness of the treatment of mycosis of the skin on the legs, vitamins, antibiotics (in case of secondary infection) and various ointments based on zinc and salicylic acid are prescribed.
You must also follow certain rules:
- The feet should be washed daily.
- Change your socks more often.
- After therapy ends, old things should be thrown away.
- Socks, tights and stockings should be washed in a separate basin.
- When a fungus is detected on the foot, treatment will be effective if closed slippers are worn.
At the end of the treatment, a scratching control study is carried out.